How to Calculate Circuit Power for Your Electrical Projects?
Calculating circuit power is essential for electrical projects. An accurate understanding of circuit power ensures efficiency and safety in operations. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), improper calculations can lead to equipment failures and increased costs. Renowned electrical engineer Dr. Emily Zhang emphasizes, "Understanding circuit power is fundamental to avoiding energy wastage."
In many projects, circuit power directly affects performance and energy consumption. The U.S. Department of Energy reports that improved circuit design can reduce energy losses by up to 30%. Miscalculations often result from overlooking components like resistors and capacitors. A small error can escalate into significant issues. Engineers must remain vigilant and consider all factors affecting circuit power.
Practitioners should always seek precision in calculations. The complexity of circuit power calculations can intimidate newcomers. Yet, mastering this skill is vital for creating reliable systems. Recognizing the intricacies of this field is crucial. Striving for accuracy helps prevent costly mistakes and enhances project outcomes.

Understanding the Basics of Electrical Power in Circuits
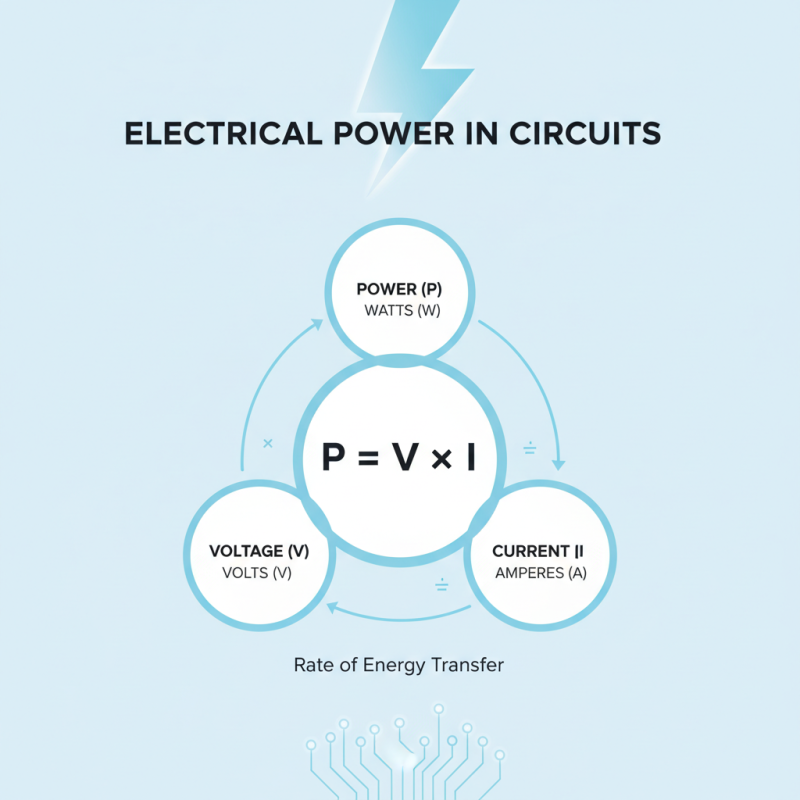
Understanding electrical power in circuits is crucial for any project. Power is the rate at which energy is transferred. In circuits, power is calculated using the formula P = V × I. Here, P is power in watts, V is voltage in volts, and I is current in amperes. This relationship highlights the connection between voltage, current, and power.
Different factors can influence circuit power. For instance, resistors affect how much current flows. A higher resistance will reduce current, thus decreasing power output. This interplay can be tricky. Sometimes, we misjudge the resistance values or how they interact with the circuit components. Testing different configurations can help identify optimal settings.
Remember, safety is essential. Always check your calculations and ensure your components can handle the power you plan to use. Mistakes in power calculations can lead to overheating or component failure. Reflecting on your circuit design can lead to better performance. Taking the time to measure and adjust can lead to successful electrical projects. Balancing power and efficiency should always be a priority.
Identifying the Key Variables in Power Calculations
Calculating circuit power begins with understanding key variables.
Voltage, current, and resistance play crucial roles.
Voltage (V) refers to the electrical pressure.
Current (I) is the flow of electric charge.
Resistance (R) measures how much a material opposes this flow.
Mastering these can simplify your projects.
Using Ohm’s Law, we find the power (P) in a circuit.
The formula is P = V × I. This shows how voltage and current interact.
You can also use P = I² × R or P = V² / R.
These formulas help in various contexts.
Challenges arise when measuring these variables accurately.
Sometimes, tools may malfunction, or connections may be loose.
Rechecking your setup can provide clarity.
Another point to consider is the unit of power: watts.
This unit measures how much energy is used over time.
It's easy to underestimate power needs.
Your circuit might require more power than initial calculations suggest.
Always account for unexpected loads.
This careful consideration can prevent circuit failures.
Step-by-Step Guide to Measuring Voltage and Current
Measuring voltage and current is essential for calculating circuit power. Begin by selecting the right multimeter. Make sure it can measure both AC and DC voltages. This tool is crucial for your electrical projects.
First, measure the voltage across the circuit. Connect the multimeter probes in parallel with the component. Watch for the reading on the display. Ensure secure connections to avoid inaccuracies. A common mistake is misplacing the probes, which can lead to faulty readings.
Next, measure the current. Set the multimeter to the current setting. Connect the probes in series with the circuit. Remember, you may need to disconnect the circuit to insert the meter. Feel free to double-check your work. Instruments can be off sometimes. Repeating measurements can help confirm the values.
Tips: Always start with a low range setting. This prevents damage to the multimeter. Understanding the readings takes practice, so don’t rush. Experiment with different circuits to build your confidence. Avoid relying solely on one source for information. Look for multiple guides to expand your knowledge.
Applying Ohm's Law to Calculate Circuit Power
Ohm's Law is fundamental for anyone working on electrical projects. It establishes the connection between voltage, current, and resistance. The formula is simple: V = IR. Here, V is voltage in volts, I is current in amperes, and R is resistance in ohms. Understanding this relationship helps in calculating circuit power effectively.
To compute power, use the equation P = VI. Power (P) is measured in watts. Break it down using Ohm’s Law. If you know the current and resistance, you can express it as P = I²R. This allows for flexibility in calculations. Each value you plug in impacts your final figure. Practicing with your circuit components will reveal discrepancies in expected versus actual power. This variance might stem from equipment tolerances.
**Tips:** Always verify the ratings of your components. Sometimes, they do not match claimed specifications. A multimeter can quickly measure current and resistance values directly. Dive into your project eyes wide open. Mistakes in calculation can lead to failed circuits or inefficient designs. Understanding every element gives clarity to your calculations. Stay cautious and double-check your work.
How to Calculate Circuit Power for Your Electrical Projects? - Applying Ohm's Law to Calculate Circuit Power
| Circuit Component | Voltage (V) | Current (I) | Power (P = V * I) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistor | 5 V | 2 A | 10 W |
| LED | 3 V | 0.02 A | 0.06 W |
| Motor | 12 V | 1.5 A | 18 W |
| Capacitor | 10 V | 0.1 A | 1 W |
| Transistor | 9 V | 0.5 A | 4.5 W |
Best Practices for Ensuring Accurate Power Measurements

Accurate power measurements are crucial for electrical projects. Ensure your methods are reliable to avoid costly mistakes. First, use the right tools. A multimeter can measure voltage and current precisely. Digital wattmeters also provide direct power readings. However, always calibrate these devices regularly. Calibration can sometimes be overlooked but is essential for accuracy.
Tips: Double-check your connections. Loose wires can lead to incorrect measurements. Make it a habit to inspect your setup before taking readings. Another common mistake is assuming all loads are purely resistive. Many devices have reactive components, which complicate calculations. Understanding this can vastly improve your results.
Try to account for efficiency losses. Not every circuit operates at 100% efficiency, especially under load variations. This aspect is often forgotten. Reflect on how your environment can affect readings too. Temperature and humidity may influence electronic components. By acknowledging these factors, your power calculations will become more accurate and reliable.
Related Posts
-

Top 5 Circuit Power Solutions Driving Efficiency in Modern Electronics
-

Best 10 Circuit Control Techniques You Need to Know for Your Projects
-

Top 10 Schneider Electric Products You Should Know About?
-

What is an Electric Motor Controller and How Does It Work?
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Best Power Controller for Your Needs
-

What is a Motor Control Circuit and How Does it Work in 2026
 Skip to content
Skip to content